The CSS Box Model
All HTML elements can be considered as boxes. In CSS, the term “box model” is used when talking about design and layout.
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around HTML elements, and it consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content.
The box model allows us to add a border around elements, and to define space between elements.
The image below illustrates the box model:
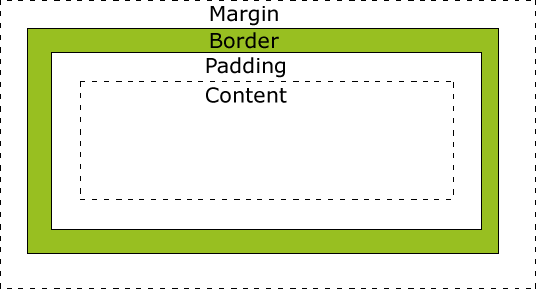
Explanation of the different parts:
- Content – The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding – Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border – A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin – Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent
Example
div { width: 300px; padding: 25px; border: 25px solid navy; margin: 25px; }
Width and Height of an Element
In order to set the width and height of an element correctly in all browsers, you need to know how the box model works.
 |
Important: When you set the width and height properties of an element with CSS, you just set the width and height of the content area. To calculate the full size of an element, you must also add padding, borders and margins. |
|---|
Let’s style a <div> element to have a total width of 350px:
Example
div { width: 320px; padding: 10px; border: 5px solid gray; margin: 0; }
Let’s do the math:
320px (width)
+ 20px (left + right padding)
+ 10px (left + right border)
+ 0px (left + right margin)
= 350px
The total width of an element should be calculated like this:
Total element width = width + left padding + right padding + left border + right border + left margin + right margin
The total height of an element should be calculated like this:
Total element height = height + top padding + bottom padding + top border + bottom border + top margin + bottom margin
Browsers Compatibility Issue
Internet Explorer 8 and earlier versions, include padding and border in the width property.
To fix this problem, add a <!DOCTYPE html> to the HTML page.
